What is a Gantry System?
Gantry systems are versatile machines at the centre of industrial automation. Gantry system application has become a must in an array of industries because of the stability, precision, and capability to carry out duties with incredible repeatability.
In this article we are going to explain what a gantry robot is, its pros and cons, and how industrial gantry robots are used today.
Definition of Gantry Robot
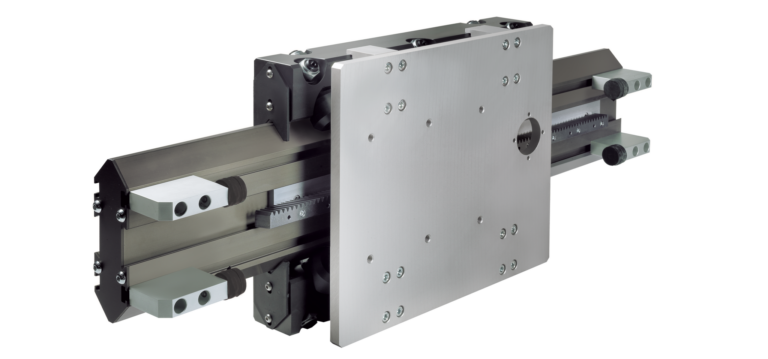
A gantry robot is a type of industrial robot, an automated piece of machinery applied in manufacturing or production, that utilizes a robot arm that is mounted either overhead on a rail system or a frame. In the gantry system, the beams hold up the robotic arm, creating an inflexible, stable structure. This arrangement allows gantry robots to move along the three linear axes: X, Y, and Z. They refer respectively to, horizontal movement from left to right, horizontal movement from the front to the back, and vertical movement up and down.
Key features of a Gantry Robot
The key features in gantry robots enable this machinery to be the best in a wide range of applications, by increasing its versatility and effectiveness.
Thanks to the multi axis structure that characterizes gantry robot design, the equipment can work in a large area with high precision, making it ideal for tasks that require extensive manipulation in a large environment. Moreover, the gantry robot structure is stable and rigid, making sure that the movements will be accurate and easily repeatable.
A gantry system is operated by a drive system and a control system, which both are used to control the movement of the robotic arm and structure and can be compared to the brain and the body of the robot. The control system, or the “brain,” uses a specialised software to program the requested application of the gantry robot. The drive system, instead, is composed of the motors and actuators of the robot which control the movement along the X, Y and Z axes. Depending on its application and the unique advantages in speed, torque, and control required, the driving system can be hydraulic, pneumatic, or electric.
One of the main features of the gantry system is a linear actuator which helps to enhance the levels of effectiveness that gantry robots have. The job of a linear actuator is to convert the rotary movement into linear motion, thus enabling the robotic arm to carry out its tasks. This feature is essential in a gantry system as it enables more efficient and controlled motions along the axes X, Y, and Z.
What are the advantages of a gantry robot?
Industrial gantry robots provide several advantages in industrial automation, and these robotic components become an essential tool for executing some of the more critical activities. Gantry robots, with their multi axis systems, ensure a high precision and consistent and reliable performance thorough all the industries in which they can be applied.
The adaptability and customisation of gantry robots design make it ideal for different applications and work environments; and its speed and low error rate increases overall productivity and reduces cycle times. Gantry robots not only help the business that decide to use them, thanks to the robot’s scalability which allows for cost-effectiveness and flexibility, but also reduce the risk of work-related injuries for employees.
What is a Gantry system used for?
Gantry systems are utilized where much precision is needed and where a task requires a repetitive motion. Out of all the industries in which gantry robots can be found, two of the most popular uses of the gantry systems are in material handling and automotive.
Material Handling: One of the most common applications for industrial gantry robots is in material handling, where they handle either over-sized or heavyweight materials. Gantry robots are perfect for moving enormous objects with high precision and at breakneck speeds; they are irreplaceable in activities like loading and unloading products. For instance, these robots have the advantage of flexibility in designing the ability of the arm to carry the load for their customization toward material handling.
Automotive: In the case of the automotive industry, gantry robots will have a significant impact on the operations concerned with painting. Industrial gantry robots can apply paint to massive structures by using a spray gun. This capability not only creates uniform coatings but also speeds up the paint process by saving time and eventually increases productivity in the automotive manufacturing cycle.
This accuracy and speed of gantry robots at work are found in many other industries. Gantry robots make the job go faster and easier by helping in many areas, from assembly lines to warehousing, to ensure maximum productivity and consistency in function.
FAQs
What is the difference between a gantry and a cartesian robot?
A cartesian robot, much like the gantry robot, has three linear axes (X, Y, Z). The cartesian robot axes, opposed to the gantry robot one, allow movement in a rectangular coordinate system for precise linear tasks.
How many axes does a gantry robot have?
A gantry robot typically has three primary linear axes (X, Y, and Z), but it can include additional axes depending on its design and application.
How much weight can a gantry robot lift?
A gantry robot’s lifting capacity can range from a few kilograms to several tons, depending on its size and application.