Packaging automation is being used by businesses who seek to better efficiency and eliminate repetitive tasks for their employees. With many businesses facing challenges of high demands and customer expectations, packaging automation is a solution to many process-related issues.
The purpose of this guide is to explain how packaging automation works, why it is used and what the latest technologies and trends are.
What is automated packing?
Automated packaging is the use of technology to carry out packing processes and tasks, which are traditionally performed manually. Automated packaging uses robotics and complex machinery to make the entire packing process more efficient.
By applying an automated packaging system to every step of the packing production, from product handling to boxing and labelling, many companies have been able to save money, assure consistency, and avoid material waste.
How does automated packing work?
To better understand how automated packaging solutions work, we need to identify the different types of packaging automation: Semi-automated packaging process and automated packaging process.
A semi-automated packaging process combines manual labour with elements of automation. One example could be when an operator oversees starting the process and an automatic packing system finishes it, or vice versa.
An automated packaging process, as the name suggests, is a process fully operated by automated packaging equipment; it is preprogrammed from start to end and is a common solution for companies where demand is high.
In each packing process, whether that is automated or not, there are similar steps. First, the products are received and are identified by barcodes, to pick on suitable packing materials and methods; they are then scanned to sort and pack the products using barcode scanning technology to ensure accuracy and traceability throughout the packing process. It will sort the products based on some criteria that may be predetermined according to size, weight, or destination for the packing process to be maximized without errors. The products are then packed in this stage into containers, sealing of packages, and application of labels by using an automated machine. Finally, the items are prepared for shipment or distribution after packing.
Benefits of automated packing
Automated packing offers businesses looking to grow or expand a lot of advantages that will help their operations, which can bring significant change both in logistics and supply chain management and customer satisfaction. The main benefit, and the most obvious one, would be speed. Automated packaging systems can pack products increasingly faster than humans and are therefore able to meet a higher demand. Packaging automation is also ideal for executing repetitive activities in that the process involves robots, which guarantee uniformity and predictability.
As far as most businesses are concerned, what makes it essential for the packaging process to be automated is that it allows them to scale their operations as the company grows and have a chance to redesign their packaging systems to handle a range of products or types of packaging in line with the market demands.
Another vital aspect of automated packaging solutions is their impact on warehouse sustainability. Thanks to packaging automation, the environmental footprint caused by warehouses can be reduced by optimizing packaging materials and eliminating excess waste. Automated processes can minimize the use of packaging materials by measuring exactly what is needed and how much of it for each product by reducing overpacking and unnecessary resource consumption.
Linear motion technology in automated packing
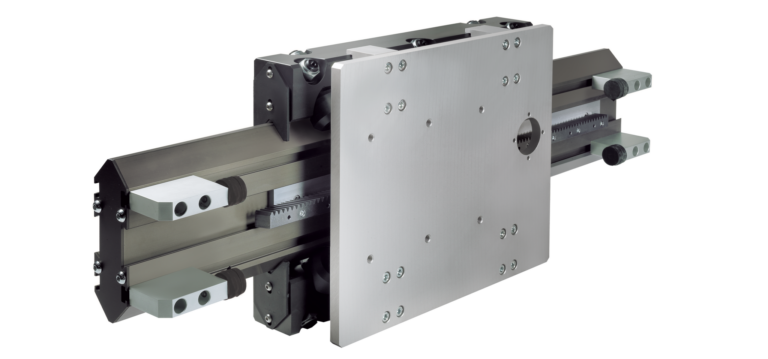
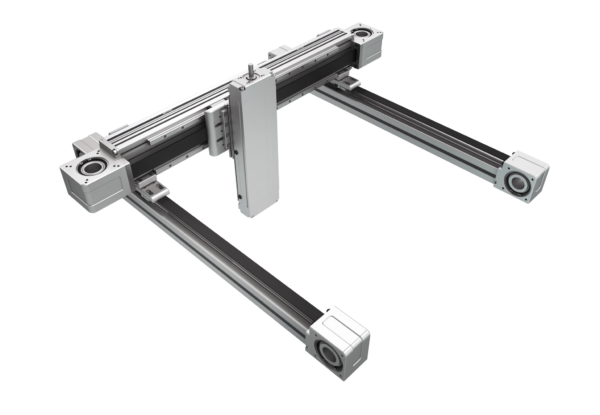
Linear technology has significantly changed automated packaging systems, enabling the industry to achieve higher operational speeds and minimize downtime. These systems play a crucial role in automated packaging by ensuring smooth and accurate linear motion with maximum precision and efficiency.
Automated packing systems typically involve wear-intensive applications characterized by high speeds and heavy rotary movements, demanding low friction and minimal maintenance. By incorporating multi-axis actuators into these systems, efficiency and reliability are significantly enhanced. Integrated actuators reduce maintenance needs, lower costs, and minimize environmental impact, ensuring optimal performance and sustainability in packaging operations.
Latest technologies in packaging automation
Packaging automation industry is evolving due to the rapid integration of state-of-the-art technologies. For example, sensors in intelligent packaging generate real-time monitoring data that assure the quality of products. AI algorithms are also shaping the future of the industry by analysing vast amounts of data to streamline packaging operations, enhancing efficiency, and minimizing waste.
Sustainability is becoming increasingly the prime concern in the packaging industry, where automation in packaging becomes widely applicable, right from manufacturing to logistic operations. By integrating automated packaging solutions, manufacturers can enhance efficiency and optimize resource utilization, contributing to their sustainability objectives while meeting consumer demands for eco-friendly packaging solutions. As the industry continues to embrace automation, it is poised to achieve greater operational excellence and environmental stewardship, ensuring a brighter and more sustainable future for packaging worldwide.
FAQs
Is AI used in automated packaging?
AI is used in automated packaging to optimize processes such as sorting, quality control, predictive maintenance to improve efficiency and reduce errors.
Which type of automation is commonly used in the packaging industry?
Robotic automation, involving robotic arms and conveyors, is commonly used in the packaging industry for tasks such as packing, palletizing, and labelling.
How many types of packaging machines are there?
Packaging machines are categorized into primary packaging (e.g., filling, wrapping, and sealing machines), secondary packaging (e.g. case packing, and bundling machines), and tertiary packaging (e.g., palletizing and stretch wrapping machines).